Green Politics on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Green politics, or ecopolitics, is a
 According to
According to 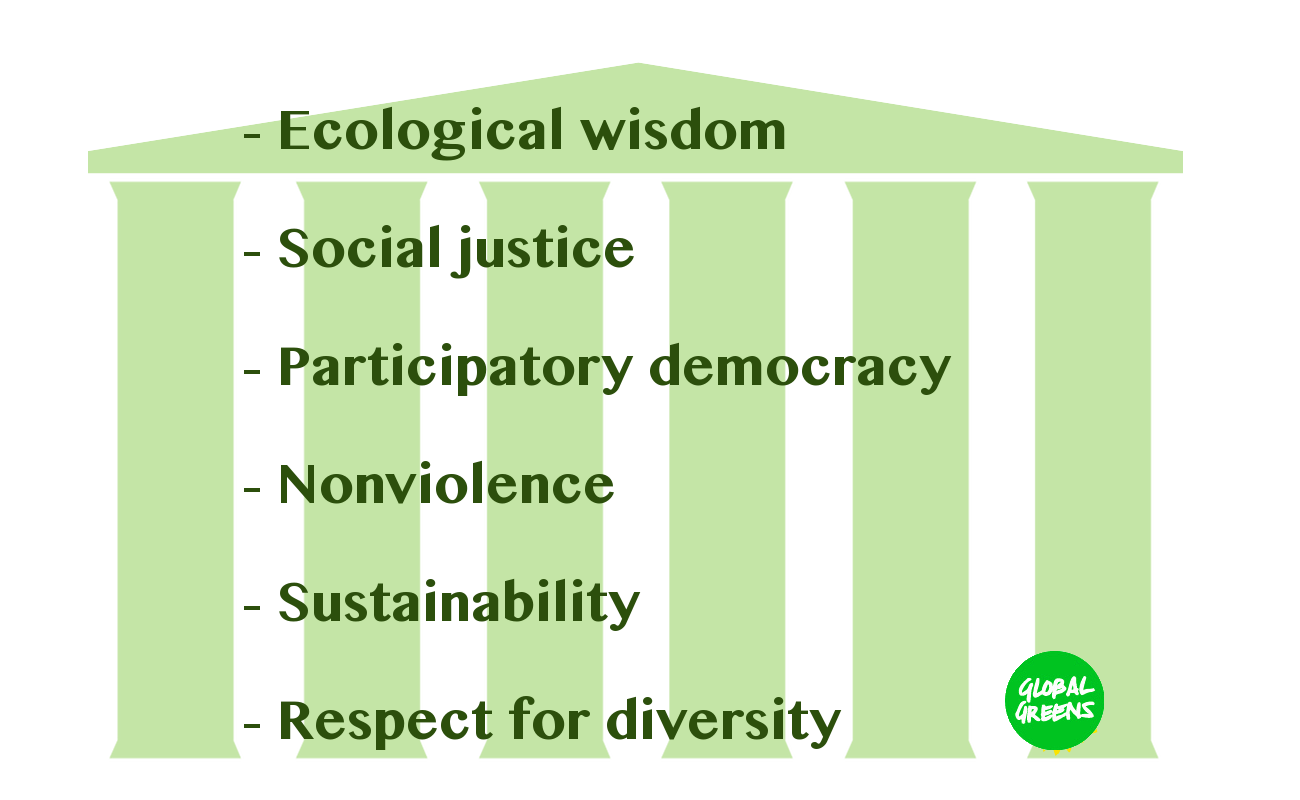 In 2001, the
In 2001, the
 Some Greens refer to
Some Greens refer to
Tim Jackson, 2017 (cropped).jpg, Tim Jackson, author of
 Since the beginning, green politics has emphasized local,
Since the beginning, green politics has emphasized local,
NLN Michael Albert.jpg, Michael Albert, theorist of participatory economics (participism)
César Rendueles durante su conferencia en Wikimanía 2015 06.JPG, César Rendueles, theorist of Common good (economics) and open content and net neutrality
AntonioNegri SeminarioInternacionalMundo.jpg, Antonio Negri, theorist of Post-fordism and immaterial labour
 Although Greens in the Green Party (United States), United States "call for an end to the 'War on Drugs'" and "for the decriminalization of victimless crimes", they also call for developing "a firm approach to law enforcement that directly addresses violent crime, including trafficking in hard drugs".
In Europe, some green parties have tended to support the creation of a democratic federal Europe, while others have opposed European integration.
In the spirit of nonviolence, green politics oppose the war on terrorism and the curtailment of civil rights, focusing instead on nurturing deliberative democracy in war-torn regions and the construction of a civil society with an increased role for women.
In keeping with their commitment to the preservation of diversity, greens are often committed to the maintenance and protection of indigenous communities, languages, and traditions. An example of this is the Green Party (Ireland), Irish Green Party's commitment to the preservation of the Irish Language. Some of the green movement has focused on divesting in fossil fuels. Academics Stand Against Poverty states "it is paradoxical for universities to remain invested in fossil fuel companies". Thomas Pogge says that the fossil fuel divestment movement can increase political pressure at events like the international climate change conference (COP). Alex Epstein of Forbes notes that it is hypocritical to ask for divestment without a boycott and that a boycott would be more effective. Some institutions that are leading by example in the academic area are Stanford University, Syracuse University, Sterling College (Vermont), Sterling College and over 20 more. A number of cities, counties and religious institutions have also joined the movement to divest.
Green politics mostly Anti-nuclear, opposes nuclear fission power and the buildup of persistent organic pollutants, supporting adherence to the precautionary principle, by which technologies are rejected unless they can be proven to not cause significant harm to the health of living things or the
Although Greens in the Green Party (United States), United States "call for an end to the 'War on Drugs'" and "for the decriminalization of victimless crimes", they also call for developing "a firm approach to law enforcement that directly addresses violent crime, including trafficking in hard drugs".
In Europe, some green parties have tended to support the creation of a democratic federal Europe, while others have opposed European integration.
In the spirit of nonviolence, green politics oppose the war on terrorism and the curtailment of civil rights, focusing instead on nurturing deliberative democracy in war-torn regions and the construction of a civil society with an increased role for women.
In keeping with their commitment to the preservation of diversity, greens are often committed to the maintenance and protection of indigenous communities, languages, and traditions. An example of this is the Green Party (Ireland), Irish Green Party's commitment to the preservation of the Irish Language. Some of the green movement has focused on divesting in fossil fuels. Academics Stand Against Poverty states "it is paradoxical for universities to remain invested in fossil fuel companies". Thomas Pogge says that the fossil fuel divestment movement can increase political pressure at events like the international climate change conference (COP). Alex Epstein of Forbes notes that it is hypocritical to ask for divestment without a boycott and that a boycott would be more effective. Some institutions that are leading by example in the academic area are Stanford University, Syracuse University, Sterling College (Vermont), Sterling College and over 20 more. A number of cities, counties and religious institutions have also joined the movement to divest.
Green politics mostly Anti-nuclear, opposes nuclear fission power and the buildup of persistent organic pollutants, supporting adherence to the precautionary principle, by which technologies are rejected unless they can be proven to not cause significant harm to the health of living things or the
File:Naomi Klein at Berkeley, California, in 2014 (cropped).jpg, Naomi Klein has written about capitalism and climate
File:Martha Nussbaum wikipedia 10-10.jpg, Martha Nussbaum, Professor of Law and Ethics at the University of Chicago, is a proponent of the Capability approach, capabilities approach to animal rights
File:Anna Grodzka.jpg, alt=Anna Grodzka, Polish green LGBTI advocate, Anna Grodzka, Polish green LGBT social movements, LGBTQIA advocate
 Green ideology emphasizes participatory democracy and the principle of "Think Globally, Act Locally, thinking globally, acting locally." As such, the ideal Green Party is thought to grow from the bottom up, from neighborhood to municipal to (eco-)regional to national levels. The goal is to rule by a consensus decision-making, consensus decision making process.
Strong local coalitions are considered a prerequisite to higher-level electoral breakthroughs. Historically, the growth of Green parties has been sparked by a single issue where Greens can appeal to ordinary citizens' concerns. In Germany, for example, the Greens' early opposition to nuclear power won them their first successes in the federal elections.
Green ideology emphasizes participatory democracy and the principle of "Think Globally, Act Locally, thinking globally, acting locally." As such, the ideal Green Party is thought to grow from the bottom up, from neighborhood to municipal to (eco-)regional to national levels. The goal is to rule by a consensus decision-making, consensus decision making process.
Strong local coalitions are considered a prerequisite to higher-level electoral breakthroughs. Historically, the growth of Green parties has been sparked by a single issue where Greens can appeal to ordinary citizens' concerns. In Germany, for example, the Greens' early opposition to nuclear power won them their first successes in the federal elections.
 There is a growing level of global cooperation between Green parties. Global gatherings of Green Parties now happen. The first Planetary Meeting of Greens was held 30–31 May 1992, in Rio de Janeiro, immediately preceding the Earth Summit (1992), United Nations Conference on Environment and Development held there. More than 200 Greens from 28 nations attended. The first formal Global Greens Gathering took place in Canberra, in 2001, with more than 800 Greens from 72 countries in attendance. The second Global Green Congress was held in São Paulo, Brazil, in May 2008, when 75 parties were represented.
Global Green networking dates back to 1990. Following the Planetary Meeting of Greens in Rio de Janeiro, a Global Green Steering Committee was created, consisting of two seats for each continent. In 1993 this Global Steering Committee met in Mexico City and authorized the creation of a Global Green Network including a Global Green Calendar, Global Green Bulletin, and Global Green Directory. The Directory was issued in several editions in the next years. In 1996, 69 Green Parties from around the world signed a common declaration opposing French nuclear testing in the South Pacific, the first statement of global greens on a current issue. A second statement was issued in December 1997, concerning the Kyoto climate change treaty.
At the 2001 Canberra Global Gathering delegates for Green Parties from 72 countries decided upon a
There is a growing level of global cooperation between Green parties. Global gatherings of Green Parties now happen. The first Planetary Meeting of Greens was held 30–31 May 1992, in Rio de Janeiro, immediately preceding the Earth Summit (1992), United Nations Conference on Environment and Development held there. More than 200 Greens from 28 nations attended. The first formal Global Greens Gathering took place in Canberra, in 2001, with more than 800 Greens from 72 countries in attendance. The second Global Green Congress was held in São Paulo, Brazil, in May 2008, when 75 parties were represented.
Global Green networking dates back to 1990. Following the Planetary Meeting of Greens in Rio de Janeiro, a Global Green Steering Committee was created, consisting of two seats for each continent. In 1993 this Global Steering Committee met in Mexico City and authorized the creation of a Global Green Network including a Global Green Calendar, Global Green Bulletin, and Global Green Directory. The Directory was issued in several editions in the next years. In 1996, 69 Green Parties from around the world signed a common declaration opposing French nuclear testing in the South Pacific, the first statement of global greens on a current issue. A second statement was issued in December 1997, concerning the Kyoto climate change treaty.
At the 2001 Canberra Global Gathering delegates for Green Parties from 72 countries decided upon a  The Gatherings also agree on organizational matters. The first Gathering voted unanimously to set up the ''Global Green Network'' (GGN). The GGN is composed of three representatives from each Green Party. A companion organization was set up by the same resolution: ''Global Green Coordination'' (GGC). This is composed of three representatives from each Federation (Africa, Europe, The Americas, Asia/Pacific, see below). Discussion of the planned organization took place in several Green Parties prior to the Canberra meeting. The GGC communicates chiefly by email. Any agreement by it has to be by unanimity of its members. It may identify possible global campaigns to propose to Green Parties worldwide. The GGC may endorse statements by individual Green Parties. For example, it endorsed a statement by the US Green Party on the Israel-Palestine conflict.
Thirdly, Global Green Gathering, Green Gatherings are an opportunity for informal networking, from which joint campaigning may arise. For example, a campaign to protect the New Caledonian coral reef, by getting it nominated for World Heritage Status: a joint campaign by the New Caledonia Green Party, New Caledonian indigenous leaders, the French Green Party, and the Australian Greens. Another example concerns Ingrid Betancourt, the leader of the Green Party in Colombia, the Green Oxygen Party (''Partido Verde Oxigeno''). Ingrid Betancourt and the party's Campaign Manager, Claire Rojas, were kidnapped by a hard-line faction of Revolutionary Armed Forces of Colombia, FARC on 7 March 2002, while travelling in FARC-controlled territory. Betancourt had spoken at the Canberra Gathering, making many friends. As a result, Green Parties all over the world have organized, pressing their governments to bring pressure to bear. For example, Green Parties in African countries, Austria, Canada, Brazil, Peru, Mexico, France, Scotland, Sweden and other countries have launched campaigns calling for Betancourt's release. Bob Brown, the leader of the Australian Greens, went to Colombia, as did an envoy from the European Federation, Alain Lipietz, who issued a report. The four Federations of Green Parties issued a message to FARC. Ingrid Betancourt was rescued by the Colombian military in Operation Jaque in 2008.
The Gatherings also agree on organizational matters. The first Gathering voted unanimously to set up the ''Global Green Network'' (GGN). The GGN is composed of three representatives from each Green Party. A companion organization was set up by the same resolution: ''Global Green Coordination'' (GGC). This is composed of three representatives from each Federation (Africa, Europe, The Americas, Asia/Pacific, see below). Discussion of the planned organization took place in several Green Parties prior to the Canberra meeting. The GGC communicates chiefly by email. Any agreement by it has to be by unanimity of its members. It may identify possible global campaigns to propose to Green Parties worldwide. The GGC may endorse statements by individual Green Parties. For example, it endorsed a statement by the US Green Party on the Israel-Palestine conflict.
Thirdly, Global Green Gathering, Green Gatherings are an opportunity for informal networking, from which joint campaigning may arise. For example, a campaign to protect the New Caledonian coral reef, by getting it nominated for World Heritage Status: a joint campaign by the New Caledonia Green Party, New Caledonian indigenous leaders, the French Green Party, and the Australian Greens. Another example concerns Ingrid Betancourt, the leader of the Green Party in Colombia, the Green Oxygen Party (''Partido Verde Oxigeno''). Ingrid Betancourt and the party's Campaign Manager, Claire Rojas, were kidnapped by a hard-line faction of Revolutionary Armed Forces of Colombia, FARC on 7 March 2002, while travelling in FARC-controlled territory. Betancourt had spoken at the Canberra Gathering, making many friends. As a result, Green Parties all over the world have organized, pressing their governments to bring pressure to bear. For example, Green Parties in African countries, Austria, Canada, Brazil, Peru, Mexico, France, Scotland, Sweden and other countries have launched campaigns calling for Betancourt's release. Bob Brown, the leader of the Australian Greens, went to Colombia, as did an envoy from the European Federation, Alain Lipietz, who issued a report. The four Federations of Green Parties issued a message to FARC. Ingrid Betancourt was rescued by the Colombian military in Operation Jaque in 2008.
 Affiliated members in Asia, Pacific and Oceania form the Asia-Pacific Green Network.
The member parties of the
Affiliated members in Asia, Pacific and Oceania form the Asia-Pacific Green Network.
The member parties of the
Global Greens Charter, Canberra 2001
{{DEFAULTSORT:Green Politics Green politics, Environmentalism Political ideologies Progressivism Anti-globalization movement History of environmentalism Articles containing video clips
political ideology
An ideology is a set of beliefs or philosophies attributed to a person or group of persons, especially those held for reasons that are not purely epistemic, in which "practical elements are as prominent as theoretical ones." Formerly applied pri ...
that aims to foster an ecologically sustainable society often, but not always, rooted in environmentalism
Environmentalism or environmental rights is a broad philosophy, ideology, and social movement regarding concerns for environmental protection and improvement of the health of the environment, particularly as the measure for this health seek ...
, nonviolence, social justice
Social justice is justice in terms of the distribution of wealth, opportunities, and privileges within a society. In Western and Asian cultures, the concept of social justice has often referred to the process of ensuring that individuals fu ...
and grassroots democracy
Grassroots democracy is a tendency towards designing political processes that shift as much decision-making authority as practical to the organization's lowest geographic or social level of organization.
Grassroots organizations can have a var ...
. Wall 2010. p. 12-13. It began taking shape in the western world in the 1970s; since then Green parties have developed and established themselves in many countries around the globe and have achieved some electoral success.
The political term green was used initially in relation to ''die Grünen Die Grünen (German for "the Greens") may refer to:
*The Greens – The Green Alternative
The Greens – The Green Alternative (german: Die Grünen – Die Grüne Alternative, ) is a green political party in Austria.
The party was founded in 19 ...
'' (German
German(s) may refer to:
* Germany (of or related to)
** Germania (historical use)
* Germans, citizens of Germany, people of German ancestry, or native speakers of the German language
** For citizens of Germany, see also German nationality law
**Ge ...
for "the Greens"), a green party formed in the late 1970s. The term political ecology is sometimes used in academic circles, but it has come to represent an interdisciplinary field of study as the academic discipline offers wide-ranging studies integrating ecological social sciences with political economy
Political economy is the study of how Macroeconomics, economic systems (e.g. Marketplace, markets and Economy, national economies) and Politics, political systems (e.g. law, Institution, institutions, government) are linked. Widely studied ph ...
in topics such as degradation and marginalization, environmental conflict
Environmental conflicts or ecological distribution conflicts (EDCs) are social conflicts caused by environmental degradation or by unequal distribution of environmental resources.Libiszewski, Stephan.What is an Environmental Conflict." ''Journal ...
, conservation and control and environmental identities and social movements.
Supporters of green politics share many ideas with the conservation
Conservation is the preservation or efficient use of resources, or the conservation of various quantities under physical laws.
Conservation may also refer to:
Environment and natural resources
* Nature conservation, the protection and managem ...
, environmental
A biophysical environment is a biotic and abiotic surrounding of an organism or population, and consequently includes the factors that have an influence in their survival, development, and evolution. A biophysical environment can vary in scale f ...
, feminist
Feminism is a range of socio-political movements and ideologies that aim to define and establish the political, economic, personal, and social equality of the sexes. Feminism incorporates the position that society prioritizes the male po ...
and peace movement
A peace movement is a social movement which seeks to achieve ideals, such as the ending of a particular war (or wars) or minimizing inter-human violence in a particular place or situation. They are often linked to the goal of achieving world peac ...
s. In addition to democracy and ecological issues, green politics is concerned with civil liberties
Civil liberties are guarantees and freedoms that governments commit not to abridge, either by constitution, legislation, or judicial interpretation, without due process. Though the scope of the term differs between countries, civil liberties may ...
, social justice, nonviolence, sometimes variants of localism and tends to support social progressivism
Progressivism holds that it is possible to improve human societies through political action. As a political movement, progressivism seeks to advance the human condition through social reform based on purported advancements in science, tech ...
. Green party platforms are largely considered left in the political spectrum
A political spectrum is a system to characterize and classify different political positions in relation to one another. These positions sit upon one or more geometric axes that represent independent political dimensions. The expressions politi ...
. The green ideology has connections with various other ecocentric political ideologies, including ecofeminism, eco-socialism
Eco-socialism (also known as green socialism or socialist ecology) is an ideology merging aspects of socialism with that of green politics, ecology and alter-globalization or anti-globalization. Eco-socialists generally believe that the expansi ...
and green anarchism, but to what extent these can be seen as forms of green politics is a matter of debate. As the left-wing
Left-wing politics describes the range of political ideologies that support and seek to achieve social equality and egalitarianism, often in opposition to social hierarchy. Left-wing politics typically involve a concern for those in soci ...
green political philosophy developed, there also came into separate existence opposite movements on the right-wing
Right-wing politics describes the range of political ideologies that view certain social orders and hierarchies as inevitable, natural, normal, or desirable, typically supporting this position on the basis of natural law, economics, authorit ...
that include ecological components such as eco-capitalism
Eco-capitalism, also known as environmental capitalism or (sometimes) green capitalism, is the view that capital exists in nature as "natural capital" (ecosystems that have ecological yield) on which all wealth depends. Therefore, governments ...
and green conservatism.
History
Influences
Adherents to green politics tend to consider it to be part of a higher worldview and not simply a political ideology. Green politics draws its ethical stance from a variety of sources, from the values ofindigenous peoples
Indigenous peoples are culturally distinct ethnic groups whose members are directly descended from the earliest known inhabitants of a particular geographic region and, to some extent, maintain the language and culture of those original people ...
, to the ethics of Mahatma Gandhi
Mohandas Karamchand Gandhi (; ; 2 October 1869 – 30 January 1948), popularly known as Mahatma Gandhi, was an Indian lawyer, anti-colonial nationalist Quote: "... marks Gandhi as a hybrid cosmopolitan figure who transformed ... anti- ...
, Baruch Spinoza
Baruch (de) Spinoza (born Bento de Espinosa; later as an author and a correspondent ''Benedictus de Spinoza'', anglicized to ''Benedict de Spinoza''; 24 November 1632 – 21 February 1677) was a Dutch philosopher of Portuguese-Jewish origin, b ...
, and Jakob von Uexküll
Jakob may refer to:
People
* Jakob (given name), including a list of people with the name
* Jakob (surname), including a list of people with the name
Other
* Jakob (band), a New Zealand band, and the title of their 1999 EP
* Max Jakob Memorial Aw ...
. These people influenced green thought in their advocacy of long-term seventh generation foresight, and on the personal responsibility of every individual to make moral choices.
Unease about adverse consequences of human actions on nature predates the modern concept of environmentalism
Environmentalism or environmental rights is a broad philosophy, ideology, and social movement regarding concerns for environmental protection and improvement of the health of the environment, particularly as the measure for this health seek ...
. Social commentators as far apart as ancient Rome and China complained of air, water and noise pollution
Noise pollution, also known as environmental noise or sound pollution, is the propagation of noise with ranging impacts on the activity of human or animal life, most of them are harmful to a degree. The source of outdoor noise worldwide is main ...
.
The philosophical roots of environmentalism can be traced back to enlightenment thinkers such as Rousseau
Jean-Jacques Rousseau (, ; 28 June 1712 – 2 July 1778) was a Genevan philosopher, writer, and composer. His political philosophy influenced the progress of the Age of Enlightenment throughout Europe, as well as aspects of the French Revolu ...
in France, and later the author and naturalist Thoreau
Henry David Thoreau (July 12, 1817May 6, 1862) was an American naturalist, essayist, poet, and philosopher. A leading transcendentalist, he is best known for his book ''Walden'', a reflection upon simple living in natural surroundings, and hi ...
in America. Organised environmentalism began in late 19th Century Europe and the United States as a reaction to the Industrial Revolution
The Industrial Revolution was the transition to new manufacturing processes in Great Britain, continental Europe, and the United States, that occurred during the period from around 1760 to about 1820–1840. This transition included going f ...
with its emphasis on unbridled economic expansion.
"Green politics" first began as conservation and preservation movements, such as the Sierra Club, founded in San Francisco in 1892.
Left-green platforms of the form that make up the green parties today draw terminology from the science of ecology
Ecology () is the study of the relationships between living organisms, including humans, and their physical environment. Ecology considers organisms at the individual, population, community, ecosystem, and biosphere level. Ecology overlaps wi ...
, and policy from environmentalism
Environmentalism or environmental rights is a broad philosophy, ideology, and social movement regarding concerns for environmental protection and improvement of the health of the environment, particularly as the measure for this health seek ...
, deep ecology, feminism
Feminism is a range of socio-political movements and ideologies that aim to define and establish the political, economic, personal, and social equality of the sexes. Feminism incorporates the position that society prioritizes the male po ...
, pacifism
Pacifism is the opposition or resistance to war, militarism (including conscription and mandatory military service) or violence. Pacifists generally reject theories of Just War. The word ''pacifism'' was coined by the French peace campaign ...
, anarchism
Anarchism is a political philosophy and movement that is skeptical of all justifications for authority and seeks to abolish the institutions it claims maintain unnecessary coercion and hierarchy, typically including, though not necessa ...
, libertarian socialism
Libertarian socialism, also known by various other names, is a left-wing,Diemer, Ulli (1997)"What Is Libertarian Socialism?" The Anarchist Library. Retrieved 4 August 2019. anti-authoritarian, anti-statist and libertarianLong, Roderick T. (2 ...
, libertarian possibilism
Libertarian possibilism ( es, posibilismo libertario) was a political current in early-20th-century Spanish anarchism that advocated achieving the anarchist ends of ending the state and capitalism by participation in structures of contemporary pa ...
, social democracy
Social democracy is a Political philosophy, political, Social philosophy, social, and economic philosophy within socialism that supports Democracy, political and economic democracy. As a policy regime, it is described by academics as advocati ...
, eco-socialism
Eco-socialism (also known as green socialism or socialist ecology) is an ideology merging aspects of socialism with that of green politics, ecology and alter-globalization or anti-globalization. Eco-socialists generally believe that the expansi ...
, and/or social ecology Social ecology may refer to:
* Social ecology (academic field), the study of relationships between people and their environment, often the interdependence of people, collectives and institutions
* Social ecology (Bookchin), a theory about the relat ...
or green libertarianism
Green libertarianism is a form of green politics. Alternately, it is a form of Libertarianism in the United States, libertarianism in which the free market provides environmentally beneficial (or benign) outcomes. Marcel Wissenburg (2009) maint ...
. In the 1970s, as these movements grew in influence, green politics arose as a new philosophy which synthesized their goals. The Green Party political movement is not to be confused with the unrelated fact that in some far-right and fascist parties, nationalism has on occasion been tied into a sort of green politics which promotes environmentalism as a form of pride in the "motherland" according to a minority of authors.
Early development
In June 1970, a Dutch group called Kabouters won 5 of the 45 seats on theAmsterdam
Amsterdam ( , , , lit. ''The Dam on the River Amstel'') is the Capital of the Netherlands, capital and Municipalities of the Netherlands, most populous city of the Netherlands, with The Hague being the seat of government. It has a population ...
Gemeenteraad (City Council), as well as two seats each on councils in The Hague
The Hague ( ; nl, Den Haag or ) is a city and municipality of the Netherlands, situated on the west coast facing the North Sea. The Hague is the country's administrative centre and its seat of government, and while the official capital of ...
and Leeuwarden
Leeuwarden (; fy, Ljouwert, longname=yes /; Stadsfries dialects, Town Frisian: ''Liwwadden''; Leeuwarder dialect: ''Leewarden'') is a List of cities in the Netherlands by province, city and Municipalities of the Netherlands, municipality in Fri ...
and one seat apiece in Arnhem
Arnhem ( or ; german: Arnheim; South Guelderish: ''Èrnem'') is a city and municipality situated in the eastern part of the Netherlands about 55 km south east of Utrecht. It is the capital of the province of Gelderland, located on both banks of ...
, Alkmaar
Alkmaar () is a city and municipality in the Netherlands, located in the province of North Holland, about 30 km north of Amsterdam. Alkmaar is well known for its traditional cheese market. For tourists, it is a popular cultural destination. The ...
and Leiden
Leiden (; in English and archaic Dutch also Leyden) is a city and municipality in the province of South Holland, Netherlands. The municipality of Leiden has a population of 119,713, but the city forms one densely connected agglomeration wit ...
. The Kabouters were an outgrowth of Provo's environmental White Plans and they proposed "Groene Plannen" ("Green Plans").
The first political party to be created with its basis in environmental issues was the United Tasmania Group
The United Tasmania Group (UTG) is generally acknowledged as the world's first Green party to contest elections. The party was formed on 23 March 1972, during a meeting of the Lake Pedder Action Committee (LPAC) at the Hobart Town Hall in order ...
, founded in Australia in March 1972 to fight against deforestation and the creation of a dam that would damage Lake Pedder
Lake Pedder, once a glacial outwash lake, is a man-made impoundment and diversion lake located in the southwest of Tasmania, Australia. In addition to its natural catchment from the Frankland Range, the lake is formed by the 1972 damming of the ...
; whilst it only gained three percent in state elections, it had, according to Derek Wall, "inspired the creation of Green parties all over the world." In May 1972, a meeting at Victoria University of Wellington
Victoria University of Wellington ( mi, Te Herenga Waka) is a university in Wellington, New Zealand. It was established in 1897 by Act of Parliament, and was a constituent college of the University of New Zealand.
The university is well kno ...
, New Zealand, launched the ''Values Party
The Values Party was a New Zealand political party. It is considered the world's first national-level environmentalist party, pre-dating the use of "Green" as a political label. It was established in May 1972 at Victoria University of Wellingto ...
'', the world's first countrywide green party to contest Parliamentary seats nationally. In November 1972, Europe's first green party, PEOPLE
A person (plural, : people) is a being that has certain capacities or attributes such as reason, morality, consciousness or self-consciousness, and being a part of a culturally established form of social relations such as kinship, ownership of pr ...
in the UK came into existence.
The German Green Party was not the first Green Party in Europe to have members elected nationally but the impression was created that they had been, because they attracted the most media attention: The German Greens
Alliance 90/The Greens (german: Bündnis 90/Die Grünen, ), often simply referred to as the Greens ( ), is a green political party in Germany. It was formed in 1993 as the merger of The Greens (formed in West Germany in 1980) and Alliance 90 (fo ...
, contended in their first national election in the 1980 federal election. They started as a provisional coalition of civic groups and political campaigns which, together, felt their interests were not expressed by the conventional parties. After contesting the 1979 European elections they held a conference which identified Four Pillars of the Green Party which all groups in the original alliance could agree as the basis of a common Party platform: welding these groups together as a single Party. This statement of principles has since been utilised by many Green Parties around the world. It was this party that first coined the term "Green" ("Grün" in German) and adopted the sunflower
The common sunflower (''Helianthus annuus'') is a large annual forb of the genus ''Helianthus'' grown as a crop for its edible oily seeds. Apart from cooking oil production, it is also used as livestock forage (as a meal or a silage plant), as ...
symbol. The term "Green" was coined by one of the founders of the German Green Party, Petra Kelly
Petra Karin Kelly (29 November 1947 – 1 October 1992) was a German Green politician and ecofeminist activist. She was a founding member of the German Green Party, the first Green party to rise to prominence both nationally in Germany and wo ...
, after she visited Australia and saw the actions of the Builders Labourers Federation
The Builders Labourers Federation (BLF) was an Australian trade union that existed from 1911 until 1972, and from 1976 until 1986, when it was permanently deregistered in various Australian states by the federal Hawke Labor government and some ...
and their green ban
A green ban is a form of strike action, usually taken by a trade union or other organised labour group, which is conducted for environmentalist or conservationist purposes. They were mainly done in Australia in the 1970s, led by the Builders Labo ...
actions. In the 1983 federal election, the Greens won 27 seats in the Bundestag
The Bundestag (, "Federal Diet") is the German federal parliament. It is the only federal representative body that is directly elected by the German people. It is comparable to the United States House of Representatives or the House of Commons ...
.
Further developments
The first Canadian foray into green politics took place in the Maritimes when 11 independent candidates (including one in Montreal and one in Toronto) ran in the 1980 federal election under the banner of the Small Party. Inspired by Schumacher's Small is Beautiful, the Small Party candidates ran for the expressed purpose of putting forward an anti-nuclear platform in that election. It was not registered as an official party, but some participants in that effort went on to form the Green Party of Canada in 1983 (the Ontario Greens and British Columbia Greens were also formed that year). Former Green Party of Canada leaderElizabeth May
Elizabeth Evans May (born June 9, 1954) is a Canadian politician, environmentalist, author, activist, and lawyer who is serving as the leader of the Green Party of Canada since 2022, and previously served as the leader from 2006 to 2019. Sh ...
was the instigator and one of the candidates of the Small Party and she was eventually elected as a member of the Green Party in 2011 Canadian federal election
The 2011 Canadian federal election was held on May 2, 2011, to elect members to the House of Commons of Canada of the 41st Canadian Parliament.
The writs of election for the 2011 election were issued by Governor General David Johnston on March ...
.
In Finland, the Green League
The Green League (VIHR, fi, Vihreä liitto , sv, Gröna förbundet), shortened to the Greens ( fi, Vihreät, sv, De Gröna), is a green political party in Finland.
Ideologically, the Green League is positioned on the centre-left of the polit ...
became the first European Green Party to form part of a state-level Cabinet in 1995. The German Greens followed, forming a government with the Social Democratic Party of Germany
The Social Democratic Party of Germany (german: Sozialdemokratische Partei Deutschlands, ; SPD, ) is a centre-left social democratic political party in Germany. It is one of the major parties of contemporary Germany.
Saskia Esken has been the ...
(the " Red-Green Alliance") from 1998 to 2005. In 2001, they reached an agreement to end reliance on nuclear power
Nuclear power is the use of nuclear reactions to produce electricity. Nuclear power can be obtained from nuclear fission, nuclear decay and nuclear fusion reactions. Presently, the vast majority of electricity from nuclear power is produced b ...
in Germany, and agreed to remain in coalition and support the German government of Chancellor Gerhard Schröder
Gerhard Fritz Kurt "Gerd" Schröder (; born 7 April 1944) is a German lobbyist and former politician, who served as the chancellor of Germany from 1998 to 2005. From 1999 to 2004, he was also the Leader of the Social Democratic Party of Germa ...
in the 2001 Afghan War. This put them at odds with many Greens worldwide, but demonstrated that they were capable of difficult political tradeoffs.
In Latvia, Indulis Emsis
Indulis Emsis (born 2 January 1952) is a Latvian biologist and politician. He was Prime Minister of Latvia for ten months in 2004, the first Green politician to lead a country in the history of the world. He was Speaker of the Saeima, the Latvia ...
, leader of the Green Party and part of the Union of Greens and Farmers
The Union of Greens and Farmers ( lv, Zaļo un Zemnieku savienība, ZZS) is an agrarian political alliance in Latvia. It is made up of the Latvian Farmers' Union, Latvian Social Democratic Workers' Party, and For Latvia and Ventspils.
It is p ...
, an alliance of a Nordic agrarian party and the Green Party, was Prime Minister of Latvia for ten months in 2004, making him the first Green
Green is the color between cyan and yellow on the visible spectrum. It is evoked by light which has a dominant wavelength of roughly 495570 nm. In subtractive color systems, used in painting and color printing, it is created by a combi ...
politician to lead a country in the history of the world. In 2015, Emsis' party colleague, Raimonds Vējonis
Raimonds Vējonis (born 15 June 1966) is a Latvian politician who served as the 9th President of Latvia from 2015 to 2019 and the president of the Latvian Basketball Association since 2020.
He is a member of the Latvian Green Party, part of the ...
, was elected President of Latvia by the Latvian parliament. Vējonis became the first green head of state
A head of state (or chief of state) is the public persona who officially embodies a state Foakes, pp. 110–11 " he head of statebeing an embodiment of the State itself or representatitve of its international persona." in its unity and l ...
worldwide.
In the German state of Baden-Württenburg, the Green Party became the leader of the coalition with the Social Democrats after finishing second in the 2011 Baden-Württemberg state election. In the following state election, 2016, the Green Party became the strongest party for the first time in a German Landtag
A Landtag (State Diet) is generally the legislative assembly or parliament of a federated state or other subnational self-governing entity in German-speaking nations. It is usually a unicameral assembly exercising legislative competence in non- ...
.
In 2016, the former leader of the Austrian Greens (1997 to 2008), Alexander Van der Bellen
Alexander Van der Bellen (; born 18 January 1944) is the current president of Austria. He previously served as a professor of economics at the University of Vienna, and after joining politics, as the spokesman of the Austrian Green Party.
...
, officially running as an independent, won the 2016 Austrian presidential election, making him the second green head of state worldwide and the first directly elected by popular vote. Van der Bellen placed second in the election's first round with 21.3% of the vote, the best result for the Austrian Greens in their history. He won the second-round run-off against the far-right Freedom Party's Norbert Hofer
Norbert Gerwald Hofer (; born 2 March 1971) is an Austrian politician who served as Leader of the Freedom Party of Austria (FPÖ) from June 2019 to June 2021. He previously was Minister for Transport, Innovation and Technology from 2017 to 2019 ...
with 53.8% of the votes, making him the first President of Austria who was not backed by either the People's Party or the Social Democratic Party.
Core tenets
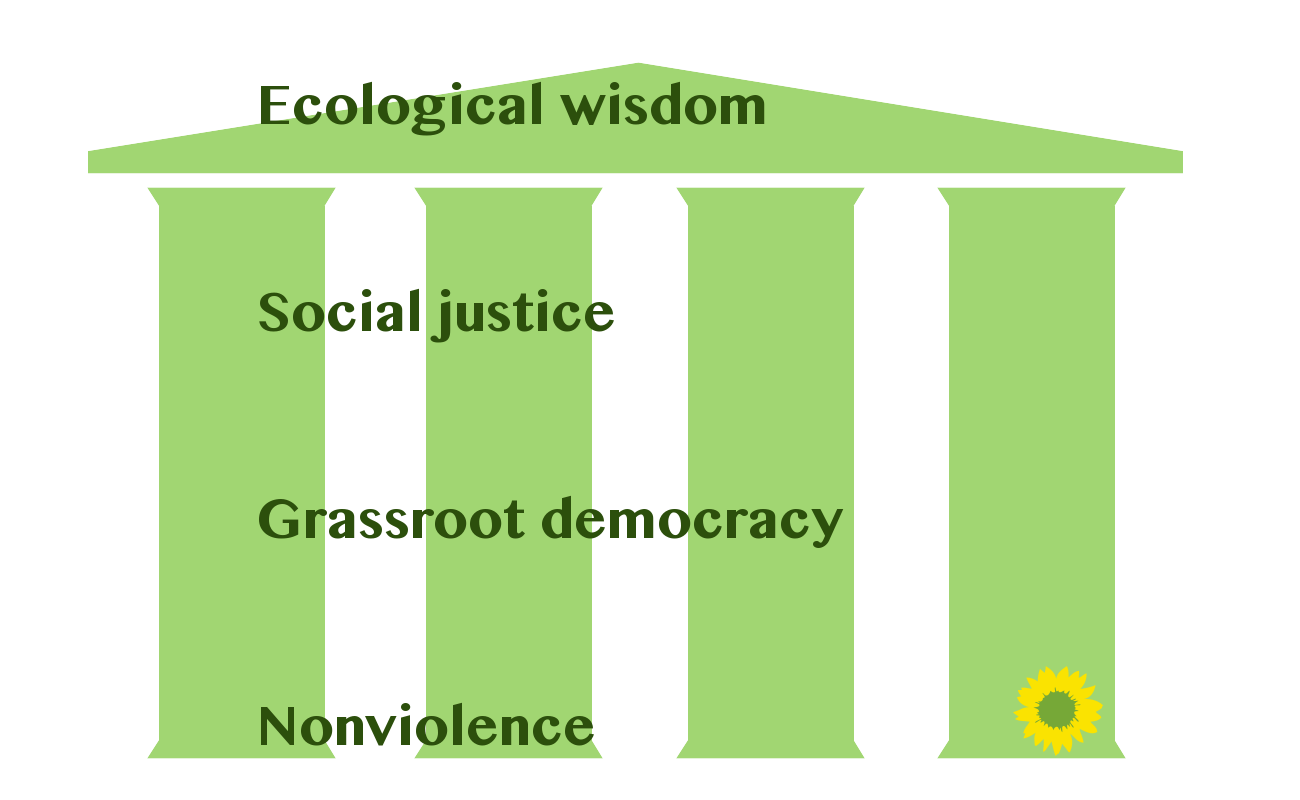
 According to
According to Derek Wall
Derek Norman Wall (born 26 May 1965) is a British politician and former member of the Green Party of England and Wales. He was the joint International Coordinator for the Green Party and stood against Prime Minister Theresa May as the Maidenhea ...
, a prominent British green proponent, there are four pillars that define green politics:
* Ecological wisdom
Ecosophy or ecophilosophy (a portmanteau of ecological philosophy) is a philosophy of ecological harmony or equilibrium. The term was coined by the French post-structuralist philosopher and psychoanalyst Félix Guattari and the Norwegian father ...
* Social justice
Social justice is justice in terms of the distribution of wealth, opportunities, and privileges within a society. In Western and Asian cultures, the concept of social justice has often referred to the process of ensuring that individuals fu ...
* Grassroots democracy
Grassroots democracy is a tendency towards designing political processes that shift as much decision-making authority as practical to the organization's lowest geographic or social level of organization.
Grassroots organizations can have a var ...
* Nonviolence
In 1984, the Green Committees of Correspondence in the United States expanded the Four Pillars into Ten Key Values, which further included:
* Decentralization
Decentralization or decentralisation is the process by which the activities of an organization, particularly those regarding planning and decision making, are distributed or delegated away from a central, authoritative location or group.
Conce ...
* Community-based economics
Community-based economics or community economics is an economic system that encourages local substitution. It is similar to the lifeways of those practicing voluntary simplicity, including traditional Mennonite, Amish, and modern eco-village commu ...
* Post-patriarchal values (later translated to ecofeminism and Ethics of care
The ethics of care (alternatively care ethics or EoC) is a normative ethical theory that holds that moral action centers on interpersonal relationships and care or benevolence as a virtue. EoC is one of a cluster of normative ethical theories tha ...
)
* Respect for diversity
* Global responsibility
* Future focus
 In 2001, the
In 2001, the Global Greens
The Global Greens (GG) is an international network of political parties and movements which work to implement the Global Greens Charter. It consists of various national Green political parties, partner networks, and other organizations associate ...
were organized as an international green movement. The Global Greens Charter
The ''Global Greens Charter'' is a document that 800 delegates from the Green parties of 72 countries decided upon a first gathering of the Global Greens in Canberra, Australia in April 2001. The first part contains six guiding principles, whereas ...
identified six guiding principles:
* Ecological wisdom
* Social justice
* Participatory democracy
Participatory democracy, participant democracy or participative democracy is a form of government in which citizens participate individually and directly in political decisions and policies that affect their lives, rather than through elected repr ...
* Nonviolence
* Sustainability
Specific definitions of sustainability are difficult to agree on and have varied in the literature and over time. The concept of sustainability can be used to guide decisions at the global, national, and individual levels (e.g. sustainable livi ...
* Respect for diversity
Ecology
Economics
Green economics focuses on the importance of the health of thebiosphere
The biosphere (from Greek βίος ''bíos'' "life" and σφαῖρα ''sphaira'' "sphere"), also known as the ecosphere (from Greek οἶκος ''oîkos'' "environment" and σφαῖρα), is the worldwide sum of all ecosystems. It can also be ...
to human well-being. Consequently, most Greens distrust conventional capitalism, as it tends to emphasize economic growth
Economic growth can be defined as the increase or improvement in the inflation-adjusted market value of the goods and services produced by an economy in a financial year. Statisticians conventionally measure such growth as the percent rate of ...
while ignoring ecological health; the " full cost" of economic growth often includes damage to the biosphere, which is unacceptable according to green politics. Green economics considers such growth to be "uneconomic growth
Uneconomic growth is economic growth that reflects or creates a decline in the quality of life. The concept is used in human development theory, welfare theory, and ecological economics. It is usually attributed to ecological economist Her ...
"— material increase that nonetheless lowers the overall quality of life. Green economics inherently takes a longer-term perspective than conventional economics, because such a loss in quality of life is often delayed. According to green economics, the present generation should not borrow from future generations, but rather attempt to achieve what Tim Jackson calls "prosperity without growth".
 Some Greens refer to
Some Greens refer to productivism
Productivism or growthism is the belief that measurable productivity and growth are the purpose of human organization (e.g., work), and that "more production is necessarily good". Critiques of productivism center primarily on the limits to g ...
, consumerism
Consumerism is a social and economic order that encourages the acquisition of goods and services in ever-increasing amounts. With the Industrial Revolution, but particularly in the 20th century, mass production led to overproduction—the supp ...
and scientism as "grey", as contrasted with "green", economic views. "Grey" approaches focus on behavioral changes.
Therefore, adherents to green politics advocate economic policies designed to safeguard the environment. Greens want governments to stop subsidizing
A subsidy or government incentive is a form of financial aid or support extended to an economic sector (business, or individual) generally with the aim of promoting economic and social policy. Although commonly extended from the government, the ter ...
companies that waste resources or pollute the natural world, subsidies that Greens refer to as "dirty subsidies". Some currents of green politics place automobile and agribusiness subsidies in this category, as they may harm human health. On the contrary, Greens look to a green tax shift
An environmental tax, ecotax (short for ecological taxation), or green tax is a tax levied on activities which are considered to be harmful to the environment and is intended to promote environmentally friendly activities via economic incentives. ...
that are seen to encourage both producers and consumers to make ecologically friendly choices.
Many aspects of green economics could be considered anti-globalist. According to many left-wing greens, economic globalization
Economic globalization is one of the three main dimensions of globalization commonly found in academic literature, with the two others being political globalization and cultural globalization, as well as the general term of globalization.
Econom ...
is considered a threat to well-being, which will replace natural environments and local cultures with a single trade economy, termed the global economic monoculture. This is not a universal policy of greens, as green liberals and green conservatives support a regulated free market
In economics, a free market is an economic system in which the prices of goods and services are determined by supply and demand expressed by sellers and buyers. Such markets, as modeled, operate without the intervention of government or any ot ...
economy with additional measures to advance sustainable development
Sustainable development is an organizing principle for meeting human development goals while also sustaining the ability of natural systems to provide the natural resources and ecosystem services on which the economy and society depend. The des ...
.
Since green economics emphasizes biospheric health and biodiversity
Biodiversity or biological diversity is the variety and variability of life on Earth. Biodiversity is a measure of variation at the genetic (''genetic variability''), species (''species diversity''), and ecosystem (''ecosystem diversity'') l ...
, an issue outside the traditional left-right spectrum, different currents within green politics incorporate ideas from socialism and capitalism. Greens on the Left are often identified as eco-socialists
Eco-socialism (also known as green socialism or socialist ecology) is an ideology merging aspects of socialism with that of green politics, ecology and alter-globalization or Anti-globalization movement, anti-globalization. Eco-socialists gener ...
, who merge ecology and environmentalism with socialism and Marxism
Marxism is a Left-wing politics, left-wing to Far-left politics, far-left method of socioeconomic analysis that uses a Materialism, materialist interpretation of historical development, better known as historical materialism, to understand S ...
and blame the capitalist system for environmental degradation, social injustice, inequality and conflict. eco-capitalists, on the other hand, believe that the free market
In economics, a free market is an economic system in which the prices of goods and services are determined by supply and demand expressed by sellers and buyers. Such markets, as modeled, operate without the intervention of government or any ot ...
system, with some modification, is capable of addressing ecological problems. This belief is documented in the business experiences of eco-capitalists in the book, ''The Gort Cloud'' that describes the gort cloud
The gort cloud is "a vast, largely invisible and growing (environmentally-aware) 'community' that sieves, measures and exchanges information on environmental (green) products and services." "The community includes NGOs, government agencies, certi ...
as the green community that supports eco-friendly businesses.
Prosperity Without Growth
''Prosperity Without Growth'' is a book by author and economist Tim Jackson. It was originally released as a report by the Sustainable Development Commission. The study rapidly became the most downloaded report in the Commission's nine-year ...
François-Bausch--w.jpg, François Bausch
François Bausch (born 16 October 1956) is a Luxembourgish politician serving as Second Deputy Prime Minister of Luxembourg since 2019. He is a member of the Chamber of Deputies as well as an alderman and member of the communal council of Lu ...
, member of ATTAC
The Association pour la Taxation des Transactions financières et pour l'Action Citoyenne (''Association for the Taxation of financial Transactions and Citizen's Action'', ATTAC) is an activist organisation originally created to promote the e ...
, theorist of the Tobin Tax
A Tobin tax was originally defined as a tax on all spot conversions of one currency into another. It was suggested by James Tobin, an economist who won the Nobel Memorial Prize in Economic Sciences. Tobin's tax was originally intended to pen ...
El periodista británico Paul Mason, fotografiado en Madrid (cropped).jpg, Paul Mason, theorist of post-capitalism
Post-capitalism is a state in which the economic systems of the world can no longer be described as forms of capitalism. Various individuals and political ideologies have speculated on what would define such a world. According to classical Marx ...
and universal basic income
Universal basic income (UBI) is a social welfare proposal in which all citizens of a given population regularly receive an unconditional transfer payment, that is, without a means test or need to work. It would be received independently of a ...
Serge Latouche - Festival Economia 2012.JPG, Serge Latouche
Serge Latouche (; ; born 12 January 1940) is a French emeritus professor of economics at the University of Paris-Sud. He holds a degree in political sciences, philosophy and economy.
Work
Latouche is a specialist in North-South economic and cul ...
, theorist of degrowth
Participatory democracy
 Since the beginning, green politics has emphasized local,
Since the beginning, green politics has emphasized local, grassroots
A grassroots movement is one that uses the people in a given district, region or community as the basis for a political or economic movement. Grassroots movements and organizations use collective action from the local level to effect change at t ...
-level political activity and decision-making. According to its adherents, it is crucial that citizens play a direct role in the decisions that influence their lives and their environment. Therefore, green politics seeks to increase the role of deliberative democracy, based on direct citizen involvement and consensus decision making, wherever it is feasible.
Green politics also encourages political action on the individual level, such as ethical consumerism, or buying things that are made according to environmentally ethical standards. Indeed, many green parties emphasize individual and grassroots action at the local and regional levels over election, electoral politics. Historically, green parties have grown at the local level, gradually gaining influence and spreading to regional or provincial politics, only entering the national arena when there is a strong network of local support.
In addition, many greens believe that governments should not levy taxes against strictly local production and trade. Some Greens advocate new ways of organizing authority to increase local control, including urban secession, bioregional democracy, and co-operative/local stakeholder ownership.
Other issues
biosphere
The biosphere (from Greek βίος ''bíos'' "life" and σφαῖρα ''sphaira'' "sphere"), also known as the ecosphere (from Greek οἶκος ''oîkos'' "environment" and σφαῖρα), is the worldwide sum of all ecosystems. It can also be ...
.
Green platforms generally favor tariffs on fossil fuels, restricting genetically modified organisms, and protections for ecoregions or communities.
The Green Party supports phasing out of nuclear power, coal, and incineration of waste. However, the Green Party in Finland has come out against its previous anti-nuclear stance and has stated that addressing global warming in the next 20 years is impossible without expanding nuclear power. These officials have proposed using Nuclear power, nuclear-generated heat to heat buildings by replacing the use of coal and biomass to reach zero-emission outputs by 2040.
Organization
Local movements
 Green ideology emphasizes participatory democracy and the principle of "Think Globally, Act Locally, thinking globally, acting locally." As such, the ideal Green Party is thought to grow from the bottom up, from neighborhood to municipal to (eco-)regional to national levels. The goal is to rule by a consensus decision-making, consensus decision making process.
Strong local coalitions are considered a prerequisite to higher-level electoral breakthroughs. Historically, the growth of Green parties has been sparked by a single issue where Greens can appeal to ordinary citizens' concerns. In Germany, for example, the Greens' early opposition to nuclear power won them their first successes in the federal elections.
Green ideology emphasizes participatory democracy and the principle of "Think Globally, Act Locally, thinking globally, acting locally." As such, the ideal Green Party is thought to grow from the bottom up, from neighborhood to municipal to (eco-)regional to national levels. The goal is to rule by a consensus decision-making, consensus decision making process.
Strong local coalitions are considered a prerequisite to higher-level electoral breakthroughs. Historically, the growth of Green parties has been sparked by a single issue where Greens can appeal to ordinary citizens' concerns. In Germany, for example, the Greens' early opposition to nuclear power won them their first successes in the federal elections.
Global organization
 There is a growing level of global cooperation between Green parties. Global gatherings of Green Parties now happen. The first Planetary Meeting of Greens was held 30–31 May 1992, in Rio de Janeiro, immediately preceding the Earth Summit (1992), United Nations Conference on Environment and Development held there. More than 200 Greens from 28 nations attended. The first formal Global Greens Gathering took place in Canberra, in 2001, with more than 800 Greens from 72 countries in attendance. The second Global Green Congress was held in São Paulo, Brazil, in May 2008, when 75 parties were represented.
Global Green networking dates back to 1990. Following the Planetary Meeting of Greens in Rio de Janeiro, a Global Green Steering Committee was created, consisting of two seats for each continent. In 1993 this Global Steering Committee met in Mexico City and authorized the creation of a Global Green Network including a Global Green Calendar, Global Green Bulletin, and Global Green Directory. The Directory was issued in several editions in the next years. In 1996, 69 Green Parties from around the world signed a common declaration opposing French nuclear testing in the South Pacific, the first statement of global greens on a current issue. A second statement was issued in December 1997, concerning the Kyoto climate change treaty.
At the 2001 Canberra Global Gathering delegates for Green Parties from 72 countries decided upon a
There is a growing level of global cooperation between Green parties. Global gatherings of Green Parties now happen. The first Planetary Meeting of Greens was held 30–31 May 1992, in Rio de Janeiro, immediately preceding the Earth Summit (1992), United Nations Conference on Environment and Development held there. More than 200 Greens from 28 nations attended. The first formal Global Greens Gathering took place in Canberra, in 2001, with more than 800 Greens from 72 countries in attendance. The second Global Green Congress was held in São Paulo, Brazil, in May 2008, when 75 parties were represented.
Global Green networking dates back to 1990. Following the Planetary Meeting of Greens in Rio de Janeiro, a Global Green Steering Committee was created, consisting of two seats for each continent. In 1993 this Global Steering Committee met in Mexico City and authorized the creation of a Global Green Network including a Global Green Calendar, Global Green Bulletin, and Global Green Directory. The Directory was issued in several editions in the next years. In 1996, 69 Green Parties from around the world signed a common declaration opposing French nuclear testing in the South Pacific, the first statement of global greens on a current issue. A second statement was issued in December 1997, concerning the Kyoto climate change treaty.
At the 2001 Canberra Global Gathering delegates for Green Parties from 72 countries decided upon a Global Greens Charter
The ''Global Greens Charter'' is a document that 800 delegates from the Green parties of 72 countries decided upon a first gathering of the Global Greens in Canberra, Australia in April 2001. The first part contains six guiding principles, whereas ...
which proposes six key principles. Over time, each Green Party can discuss this and organize itself to approve it, some by using it in the local press, some by translating it for their web site, some by incorporating it into their manifesto, some by incorporating it into their constitution. This process is taking place gradually, with online dialogue enabling parties to say where they are up to with this process.
 The Gatherings also agree on organizational matters. The first Gathering voted unanimously to set up the ''Global Green Network'' (GGN). The GGN is composed of three representatives from each Green Party. A companion organization was set up by the same resolution: ''Global Green Coordination'' (GGC). This is composed of three representatives from each Federation (Africa, Europe, The Americas, Asia/Pacific, see below). Discussion of the planned organization took place in several Green Parties prior to the Canberra meeting. The GGC communicates chiefly by email. Any agreement by it has to be by unanimity of its members. It may identify possible global campaigns to propose to Green Parties worldwide. The GGC may endorse statements by individual Green Parties. For example, it endorsed a statement by the US Green Party on the Israel-Palestine conflict.
Thirdly, Global Green Gathering, Green Gatherings are an opportunity for informal networking, from which joint campaigning may arise. For example, a campaign to protect the New Caledonian coral reef, by getting it nominated for World Heritage Status: a joint campaign by the New Caledonia Green Party, New Caledonian indigenous leaders, the French Green Party, and the Australian Greens. Another example concerns Ingrid Betancourt, the leader of the Green Party in Colombia, the Green Oxygen Party (''Partido Verde Oxigeno''). Ingrid Betancourt and the party's Campaign Manager, Claire Rojas, were kidnapped by a hard-line faction of Revolutionary Armed Forces of Colombia, FARC on 7 March 2002, while travelling in FARC-controlled territory. Betancourt had spoken at the Canberra Gathering, making many friends. As a result, Green Parties all over the world have organized, pressing their governments to bring pressure to bear. For example, Green Parties in African countries, Austria, Canada, Brazil, Peru, Mexico, France, Scotland, Sweden and other countries have launched campaigns calling for Betancourt's release. Bob Brown, the leader of the Australian Greens, went to Colombia, as did an envoy from the European Federation, Alain Lipietz, who issued a report. The four Federations of Green Parties issued a message to FARC. Ingrid Betancourt was rescued by the Colombian military in Operation Jaque in 2008.
The Gatherings also agree on organizational matters. The first Gathering voted unanimously to set up the ''Global Green Network'' (GGN). The GGN is composed of three representatives from each Green Party. A companion organization was set up by the same resolution: ''Global Green Coordination'' (GGC). This is composed of three representatives from each Federation (Africa, Europe, The Americas, Asia/Pacific, see below). Discussion of the planned organization took place in several Green Parties prior to the Canberra meeting. The GGC communicates chiefly by email. Any agreement by it has to be by unanimity of its members. It may identify possible global campaigns to propose to Green Parties worldwide. The GGC may endorse statements by individual Green Parties. For example, it endorsed a statement by the US Green Party on the Israel-Palestine conflict.
Thirdly, Global Green Gathering, Green Gatherings are an opportunity for informal networking, from which joint campaigning may arise. For example, a campaign to protect the New Caledonian coral reef, by getting it nominated for World Heritage Status: a joint campaign by the New Caledonia Green Party, New Caledonian indigenous leaders, the French Green Party, and the Australian Greens. Another example concerns Ingrid Betancourt, the leader of the Green Party in Colombia, the Green Oxygen Party (''Partido Verde Oxigeno''). Ingrid Betancourt and the party's Campaign Manager, Claire Rojas, were kidnapped by a hard-line faction of Revolutionary Armed Forces of Colombia, FARC on 7 March 2002, while travelling in FARC-controlled territory. Betancourt had spoken at the Canberra Gathering, making many friends. As a result, Green Parties all over the world have organized, pressing their governments to bring pressure to bear. For example, Green Parties in African countries, Austria, Canada, Brazil, Peru, Mexico, France, Scotland, Sweden and other countries have launched campaigns calling for Betancourt's release. Bob Brown, the leader of the Australian Greens, went to Colombia, as did an envoy from the European Federation, Alain Lipietz, who issued a report. The four Federations of Green Parties issued a message to FARC. Ingrid Betancourt was rescued by the Colombian military in Operation Jaque in 2008.
Global Green meetings
Separately from the Global Green Gatherings, ''Global Green Meetings'' take place. For instance, one took place on the fringe of the World Summit on Sustainable Development in Johannesburg. Green Parties attended from Australia, Taiwan, Korea, South Africa, Mauritius, Uganda, Cameroon, Republic of Cyprus, Italy, France, Belgium, Germany, Finland, Sweden, Norway, the US, Mexico and Chile. The Global Green Meeting discussed the situation of Green Parties on the African continent; heard a report from Mike Feinstein, former Mayor of Santa Monica, California, Santa Monica, about setting up a web site of the GGN; discussed procedures for the better working of the GGC; and decided two topics on which the Global Greens could issue statements in the near future: Iraq and the 2003 WTO meeting in Cancun.Green federations
Global Greens
The Global Greens (GG) is an international network of political parties and movements which work to implement the Global Greens Charter. It consists of various national Green political parties, partner networks, and other organizations associate ...
are organised into four continental federations:
* Federation of Green Parties of Africa
* Federation of the Green Parties of the Americas, Federation of the Green Parties of the Americas / Federación de los Partidos Verdes de las Américas
* Asia-Pacific Green Network
* European Green Party
The European Federation of Green Parties formed itself as the European Green Party on 22 February 2004, in the run-up to European Parliament elections in June 2004, a further step in trans-national integration.
Green political parties
Green movements are calling for social change to reduce the misuse of natural resources. These include grassroots non-governmental organizations like Greenpeace and green parties: * Alliance 90/The Greens * Australian Greens * The Greens – The Green Alternative, Austrian Green Party * Belarusian Green Party * Democratic Renewal of Macedonia * Dialogue for Hungary, LMP – Hungary's Green Party * Ecologist Greens * Europe Ecology – The Greens (France) * Federation of the Greens * Green League, Green League (Finland) * Greens of Andorra * Green Party of Aotearoa New Zealand * Green Party of Armenia * Green Party (Brazil) * Green Party of Canada * Green Party (Czech Republic) * Green Party of England and Wales * Green Party (Ireland) * Green Party (Israel) * Green Party of Lebanon * Green Party (Norway) * Green Party (Sweden) * Green Party (Romania) * Green Party Taiwan, Green Party of Taiwan * Green Party (Turkey) * Green Party of the United States * Groen (political party), Groen, Ecolo * GroenLinks * Hariyali Nepal Party * Latvian Green Party * Left-Green Movement * Meretz, Meretz (Israel) * Red–Green Alliance (Denmark) * Scottish Greens, Scottish Green Party * Socialist People's Party (Denmark) * The Alternative (Denmark)See also
* Outline of green politics (list of related articles, organized for easy browsing)Notes
References
*Further reading
* Dobson, Andrew (2007). ''Green Political Thought''. 4. Edition (1. Edition 1980), London/ New York: Routledge. (Hardcover) * * Spretnak, Charlene (1986). ''The Spiritual Dimension of Green Politics''. Santa Fe, N.M.: Bear & Co. 95 p.External links
Global Greens Charter, Canberra 2001
{{DEFAULTSORT:Green Politics Green politics, Environmentalism Political ideologies Progressivism Anti-globalization movement History of environmentalism Articles containing video clips